The motor, an integral component paramount to modern industry, serves the crucial role of powering various mechanical devices. The escalating workload and operational speed of motors lead to a commensurate increase in heat production during operation. Any inability to effectively dissipate this excessive heat may result in overheating – subsequently causing malfunctions or even severe damage. Consequently, providing adequate cooling for motors has emerged as a critical aspect for ensuring their regular and uninterrupted performance.
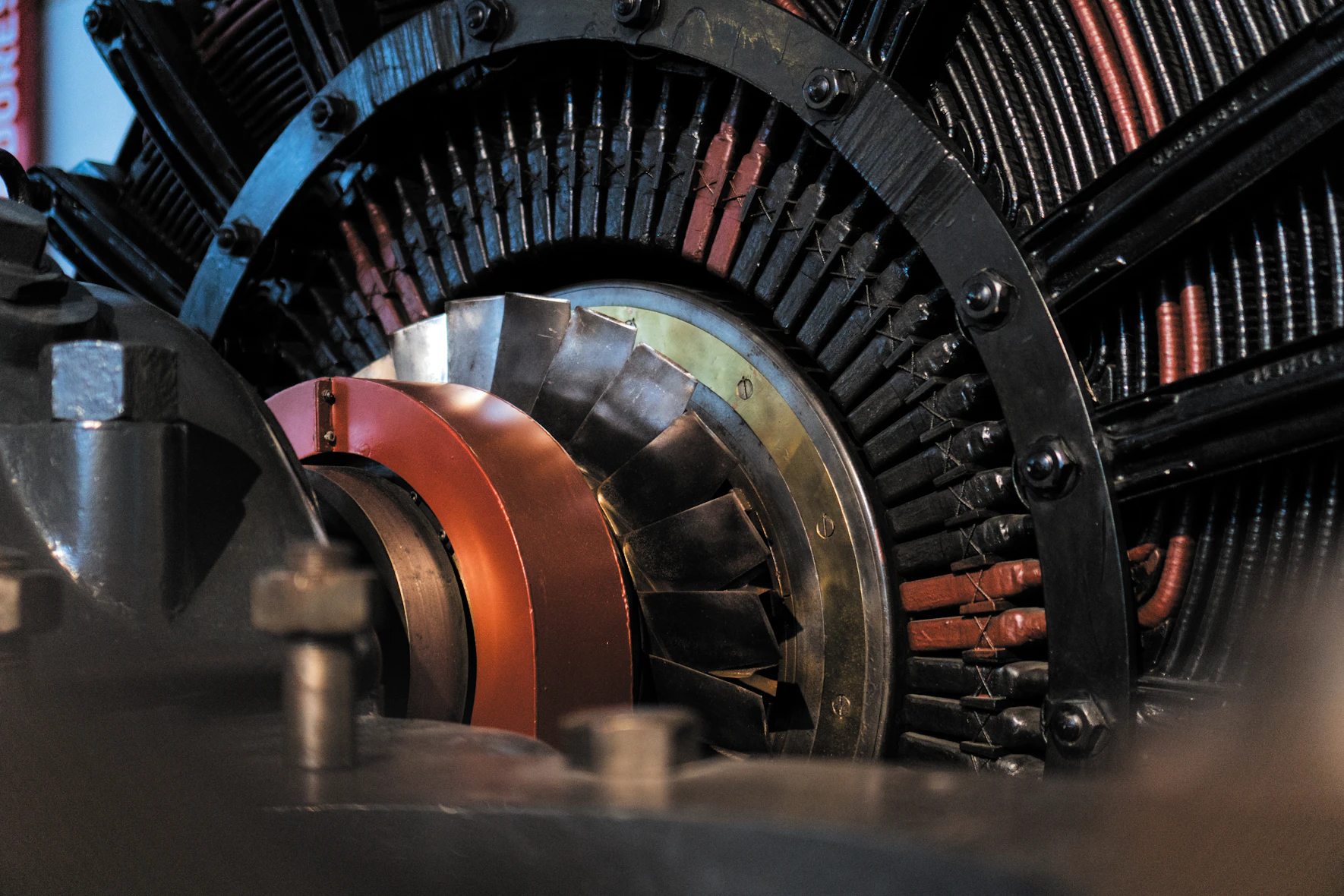
Motors generate heat when they work, and overheating can lead to motor damage. As the motor’s workload increases and its operating speed increases, the current inside the motor increases accordingly, causing more energy to be converted into heat. If this excess heat is not discharged efficiently, the temperature of the motor will continue to rise, which in turn will cause a series of problems. Here are a few of the main reasons why motor cooling is needed:
In the course of operation, motors can be exposed to elevated temperatures. Excessive heat levels could jeopardize the motor’s insulation integrity, potentially leading to insulation loss or total system failure. Additionally, overheating triggers expansion and inflicts thermal stress on the internal components of the motor. This may precipitate damage, deformity, or fracture of these crucial parts. Employing a cooling strategy for the motor enables it to operate within an optimal temperature band—which not only enhances its reliability but also extends its lifespan.
Excessive temperatures can lead to an increase in the internal resistance of the motor and influence current density, which will decrease the efficiency of the motor. Proper cooling of motors can reduce the temperature, improve the efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Overheating will accelerate the aging and wear of motor parts, increasing the frequency and cost of motor maintenance. With right motor cooling, users can effectively reduce the running temperature of the motor, slow down the aging speed of the parts.
Some special working environments, such as high-temperature environments, enclosed spaces or high-altitude areas, the motor is easily affected by the external environment and overheating. Through reasonable cooling measures, it can help the motor adapt to a variety of harsh environmental conditions and maintain stable performance.
Different motor cooling methods have their own applicable conditions and advantages. By choosing the right type of motor cooling, users can protect their motor.
Natural cooling stands out as the most straightforward and cost-effective method for motor cooling. It operates by leveraging the motor’s heat generation, transferring it to the surrounding air, and relying on natural convection to disperse the heat. The simplicity of this approach lies in its minimal requirements for additional equipment or infrastructure, making it an economical choice for many applications.
However, despite its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, natural cooling does come with limitations. Primarily, its effectiveness is constrained by the power and speed of the motor. As motors with higher power outputs and operational speeds generate more heat, natural convection alone may not suffice to adequately dissipate this heat. Consequently, there is a risk of insufficient cooling, which can impact the stability and longevity of the motor. This limitation makes natural cooling more suitable for smaller, low-power motor applications where heat generation is relatively modest.Nevertheless, natural cooling remains a viable option for many industrial settings, particularly those with low-power motor requirements or where cost considerations are paramount.
Water cooling is a method of cooling a motor through water circulation. Specifically, the water carries away the heat generated by the motor by flowing between the motor casing and the internal heat sink, and then discharges it through a circulation pipe. Water-cooled motors typically use a cooling tower or heat exchanger for the cooling operation.
Water-cooled motors provide higher cooling efficiencies than other cooling methods, resulting in more stable motor operation. Compared with other methods, water cooling has less noise and can be adapted to high power and high speed motor applications.
Air cooling is a method of cooling a motor by natural convection or forced fan cooling. Air-cooled motors are cooled by drawing in ambient air through vents and fans. Some higher-end air-cooled motors are also equipped with electronic controllers to automatically adjust the fan speed for optimal cooling.
Air-cooled motors do not require additional cooling media and can directly utilize the surrounding air to achieve cooling; at the same time, this approach has the advantages of high reliability and low maintenance costs. The disadvantage is the need to consider the impact of the environment on the motor, such as dust, humidity, etc., as well as possible noise problems. Air-cooled motors are typically used in small to medium power and low to medium speed applications, such as small machinery.
Oil cooling is a method of cooling a motor by circulating a stream of oil. Specifically, a radiator inside the motor is connected to the motor casing through the oil flow. The hot oil is then transferred to a tank or circulator and carried away by the radiator. Oil-cooled motors typically use fans and heat sinks for cooling operations.
Oil-cooled motors provide more consistent temperatures because the oil flow effectively absorbs heat; they also reduce motor noise and can accommodate high power and high speed motor applications. Oil-cooled motors are typically used in applications that require higher power and speed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, motor cooling technology plays an essential role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of motors across various industrial applications. The selection of appropriate cooling methods, such as natural cooling, water cooling, air cooling, and oil cooling, is critical in managing the heat generated during motor operation. Each cooling method offers unique advantages and is suited to different operational conditions and motor specifications.
For instance, natural cooling is cost-effective and straightforward but may not suffice for high-power applications due to its limited heat dissipation capacity. Water cooling, on the other hand, provides higher cooling efficiency and is suitable for high-power, high-speed motors, though it requires a cooling tower or heat exchanger. Air cooling, utilizing ambient air through vents and fans, offers high reliability and low maintenance costs, making it ideal for small to medium-power applications, despite potential environmental impacts like dust and humidity. Oil cooling ensures consistent temperatures and reduces motor noise, catering to high-power and high-speed motor applications but necessitating a circulator and radiator.
By effectively managing motor temperature through these cooling techniques, motors are safeguarded from thermal damage, efficiency is enhanced, maintenance cycles are extended, and adaptability to harsh environments is improved. As industrial demands on motors continue to grow, the advancement of cooling technologies will be crucial in supporting the longevity and performance of these indispensable machines, ultimately contributing to broader industrial and societal progress.
Choosing the right brand is just as important as choosing the right cooling method.Because of the advanced cooling system, ENNENG’s motor has strong durability
ENNENG is a company that specializes in the research and development of various types of permanent magnet motors. These motors are known for their exceptional durability and longevity.
ENNENG’s motors are designed with high-quality materials and advanced engineering techniques, ensuring their ability to withstand harsh operating conditions. Whether it is in gold mines, coal mines, tire factories, oil wells, or water treatment plants, ENNENG motors have proven to be highly durable and reliable.
Additionally, ENNENG motors are built with robust components and have a reduced number of moving parts. This design feature minimizes wear and tear, resulting in extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements.
Furthermore, ENNENG motors are equipped with efficient cooling systems, such as air cooling, water cooling, or air-water cooling. These cooling methods effectively dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing overheating and further contributing to the motors’ durability.
In summary, ENNENG motors are renowned for their durability due to their high-quality construction, robust components, and efficient cooling systems. These motors are built to last, providing long-term reliability and performance in various industrial applications.