PREVIEW
What is BLDC motor?
A BLDC motor is an electric motor that operates using a magnet-based rotor and electronic commutation, instead of brushes and a mechanical commutator like in traditional brushed motors. Here’s a summary of the key points:
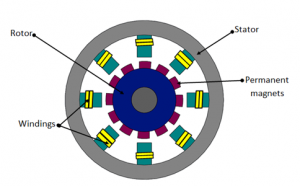
A BLDC motor consists of a stationary stator with windings and a rotor that contains permanent magnets. The stator windings are used to create a rotating magnetic field.
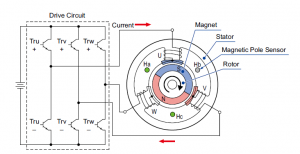
In a BLDC motor, the commutation is electronically controlled using sensors or Hall effect devices. These sensors detect the position of the rotor magnets and provide signals to the motor controller, enabling the controller to switch the power to the stator windings at the correct timing, resulting in smooth rotation.
They have higher efficiency, better power-to-weight ratio, and longer lifespan compared to brushed motors. BLDC motors also eliminate the need for brushes, reducing maintenance requirements and minimizing electrical noise and wear. Additionally, they provide precise control over speed and direction due to their electronic commutation.
Major differences between this two types of motor
Here are the major differences between the two:
With a permanent magnet rotor and stator winding, BLDC motors and PMSM motors are built similarly. The design of the rotor magnets, however, is where the main distinction lies. In contrast to PMSM motors, which have permanent magnets implanted in the stator, BLDC motors have their permanent magnets on the rotor.
BLDC motors employ electronic commutation to determine the position of the rotor and regulate the current in the windings using sensors or sensorless methods. This effectively transforms them into “DC” motors because the commutation is carried out electronically. PMSM motors, on the other hand, rely on the location of the permanent magnets on the rotor to create a spinning magnetic field. This means that a controller or encoder is used to synchronize the commutation with the rotor position.
BLDC motors are commonly used in applications that require variable speed control and good efficiency such as electric vehicles, drones, and computer peripherals. PMSM motors, on the other hand, are often found in high-performance industrial automation, robotics, and servo motor applications where precise position control and high torque density are crucial.
Due to the requirement for exact commutation timing, which is achieved through the use of sensors or sophisticated algorithms for sensorless control, BLDC motors often require a more complex control system. Inherently synchronous PMSM motors, as their name suggests, make the control algorithm simpler and enable more effective operation.
PMSM motors generally have lower torque ripple compared to BLDC motors. The torque ripple refers to the variation in torque produced during motor rotation. This reduced ripple in PMSM motors helps in achieving smoother operation, reduced vibration, and noise.